HTML5元素定位
編輯:CSS特效代碼
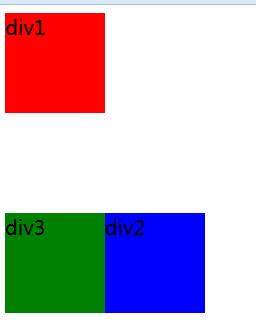
1.相對定位
position:relative
a.不影響元素本身特性
b.元素不脫離文檔流
c.如果沒有定位偏移量,對元素本身沒有任何影響
d.定位元素位置控制:top/bottom/left/right
<div class="box1">div1</div>
<div class="box2">div2</div>
<div class="box3">div3</div>
.box1{width:100px;height:100px; background:red;}
.box2{width:100px;height:100px;background:blue; position:relative;left:100px;top:100px;}
.box3{width:100px;height:100px;background:green;}
2.決定定位
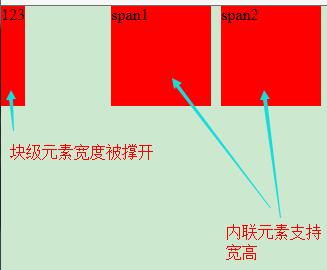
position:absolute
a.使元素完全脫離文檔流
b.使內聯元素支持寬高
c.快屬性標簽內容撐開寬度
<div class="box1">123</div>
<span class="box2">span1</span>
<span class="box3">span2</span>
.box1{height: 100px;position: absolute;top: 0;left: 0; background: red;}
.box2{width: 100px; height: 100px; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 110px; background: red;}
.box3{width: 100px; height: 100px; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 220px; background: red;}
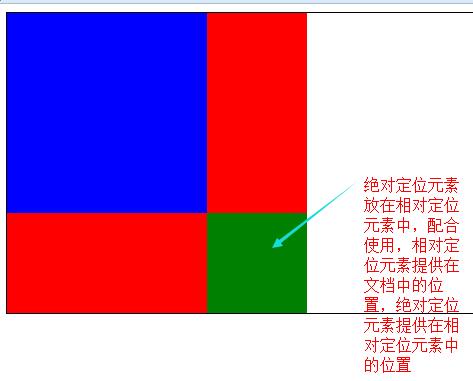
d.如果有父級則相對於父級發生偏移,如果沒有父級則相對整個文檔發生偏移
f.相對定位一般是配合絕對定位使用
<div class="box1"><!-- 定位父級 -->
<div class="box2"><!-- 結構父級 -->
<div class="box3"></div><!-- 絕對定位元素 -->
</div>
</div>
.box1{width:300px;height:300px; background:red; position:relative;}
.box2{width:200px;height:200px;background:blue;}
.box3{width:100px;height:100px;background:green; position:absolute;right:0;bottom:0;}
4.定位層級
規則:1.默認是文檔流後面的元素高於文檔流前面的元素
2.z-index:[num]:控制定位層級
- 上一頁:CSS選擇器Ⅲ
- 下一頁:CSS實現div的高度填滿剩余空間
小編推薦
熱門推薦